What is Output Devices in Electronics?
Definition
- Output devices are electronic hardware that display, produce, or act upon information generated by a system.
- They convert digital signals into real‑world formats like text, images, audio, or mechanical motion.
- They are the counterpart to input devices: input devices feed data into a system, while output devices present the results.
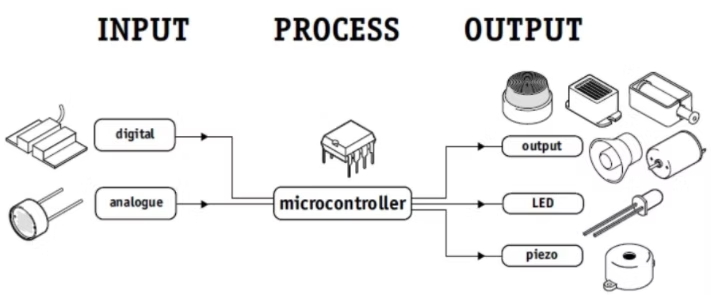
Example
Types of Output Devices in Electronics
1. Visual Output Devices
These display information in a form that can be seen.
- Monitors: LCD, LED, OLED screens used in computers and embedded systems.
- Projectors: Display visuals on large surfaces for presentations or entertainment.
- LCD/OLED Displays: Used in microcontroller projects to show characters, graphics, or sensor data.
- LED Indicators: Simple visual feedback (e.g., status lights, blinking alerts).
2. Auditory Output Devices
These produce sound signals.
- Speakers: Convert electrical signals into audible sound.
- Buzzers: Emit tones or alerts in embedded systems.
- Headphones: Personal audio output for computers or mobile devices.
3. Hard Copy Output Devices
These produce physical copies of digital data.
- Printers: Inkjet, laser, or thermal printers for documents and images.
- Plotters: Used for technical drawings and CAD outputs.
4. Physical/Mechanical Output Devices
These perform physical actions based on electronic signals.
- Motors: DC, stepper, or servo motors used in robotics and automation.
- Actuators: Convert signals into motion (e.g., solenoids, pneumatic actuators).
- Relays: Switch high-power devices based on control signals.